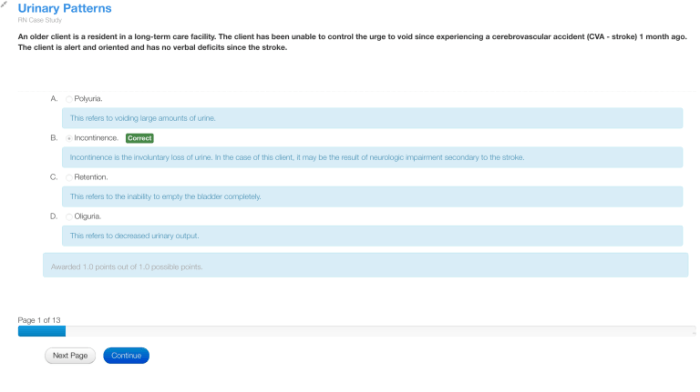
Urinary patterns HESI case study: embarking on a journey into the realm of urinary health, deciphering patterns, and unraveling their significance in assessing overall well-being. This in-depth analysis delves into the intricacies of urinary patterns, exploring their implications and providing invaluable insights for healthcare professionals.
Urinary patterns serve as a window into our health, offering a wealth of information about our hydration status, kidney function, and potential underlying medical conditions. By examining frequency, volume, and color, we can gain valuable clues about our urinary health and identify any abnormalities that may require further investigation.
Urinary Patterns: Definitions and Significance
Urinary patterns provide valuable insights into an individual’s overall health. They reflect the body’s fluid balance, kidney function, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions.
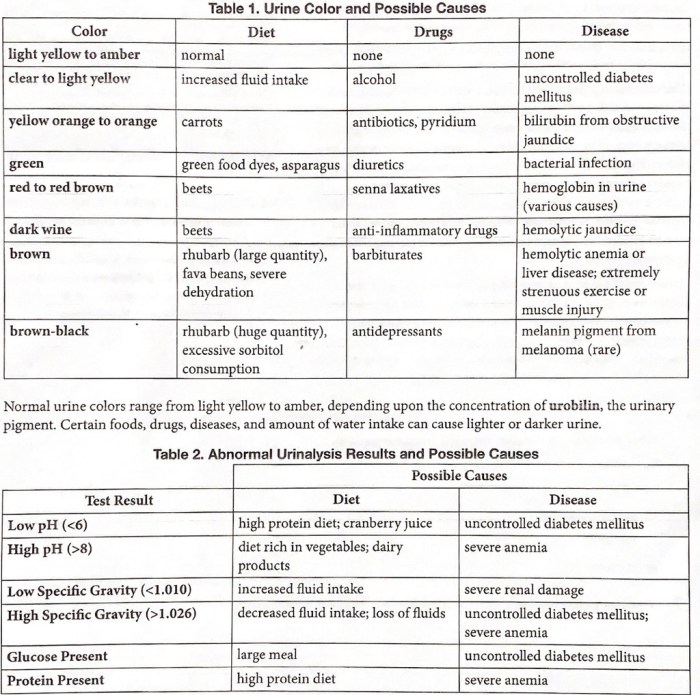
Common urinary patterns include frequency, volume, and color. Normal urinary frequency varies depending on fluid intake and individual factors, but generally falls within the range of 6-8 times per day. Urine volume should typically be around 1-2 liters per day.
Color variations can indicate hydration levels, with pale yellow urine indicating adequate hydration and darker urine suggesting dehydration.
Abnormal urinary patterns can signal underlying health issues. Frequent urination, urgency, and burning can indicate a urinary tract infection (UTI). Increased urine volume and thirst may be associated with diabetes, while decreased urine output can be a sign of kidney disease.
Methods for Assessing Urinary Patterns
Various methods are available to assess urinary patterns:
- Urine Dipsticks:Simple and inexpensive tests that detect the presence of substances such as glucose, protein, and blood in urine.
- 24-Hour Urine Collections:Collect all urine produced over a 24-hour period to measure volume and analyze specific components.
Each method has its advantages and limitations. Urine dipsticks provide quick and easy screening, but may not detect all abnormalities. 24-Hour urine collections offer more comprehensive data, but require patient cooperation and can be time-consuming.
Proper sample collection and interpretation are crucial. Patients should avoid caffeine and alcohol before urine collection, and samples should be refrigerated or kept on ice until analysis.
Factors Influencing Urinary Patterns: Urinary Patterns Hesi Case Study
Several factors can influence urinary patterns:
- Hydration:Adequate fluid intake promotes urine production and pale yellow color, while dehydration leads to decreased urine output and darker color.
- Diet:Certain foods, such as asparagus and beets, can alter urine color and odor.
- Medications:Some medications, like diuretics, can increase urine output, while others may decrease it.
- Underlying Medical Conditions:Diabetes, kidney disease, and urinary tract infections can all impact urinary patterns.
Understanding the potential impact of these factors is essential for accurate interpretation of urinary patterns.
Urinary Patterns in Specific Conditions
Urinary patterns can provide valuable information in diagnosing and monitoring specific health conditions:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs), Urinary patterns hesi case study
UTIs are characterized by frequent urination, urgency, burning, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
Diabetes
Increased urine volume, thirst, and frequent urination are common symptoms of diabetes, as the body tries to eliminate excess glucose through urine.
Kidney Disease
Decreased urine output, dark or foamy urine, and the presence of protein or blood in urine can indicate kidney dysfunction.
Nursing Implications and Interventions
Nurses play a crucial role in assessing and managing urinary patterns:
- Assessment:Nurses monitor urinary frequency, volume, and color, and collect urine samples for analysis.
- Education:Nurses educate patients on the importance of hydration, proper urine collection techniques, and potential implications of abnormal urinary patterns.
- Interventions:Nurses implement interventions to promote healthy urinary patterns, such as hydration counseling and bladder training exercises.
By understanding and interpreting urinary patterns, nurses can identify and address underlying health concerns, promote patient well-being, and contribute to effective healthcare outcomes.
FAQ Overview
What are the common methods for assessing urinary patterns?
Urine dipsticks and 24-hour urine collections are widely used methods for assessing urinary patterns, providing insights into specific parameters such as pH, glucose, and protein levels.
How can urinary patterns indicate underlying health conditions?
Abnormal urinary patterns, such as increased frequency, urgency, or changes in color, can be indicative of urinary tract infections, diabetes, kidney disease, or other health concerns, warranting further evaluation.
What role do nurses play in managing urinary patterns?
Nurses play a crucial role in assessing and managing urinary patterns, providing education on healthy hydration practices, implementing bladder training techniques, and monitoring for any signs of urinary dysfunction.