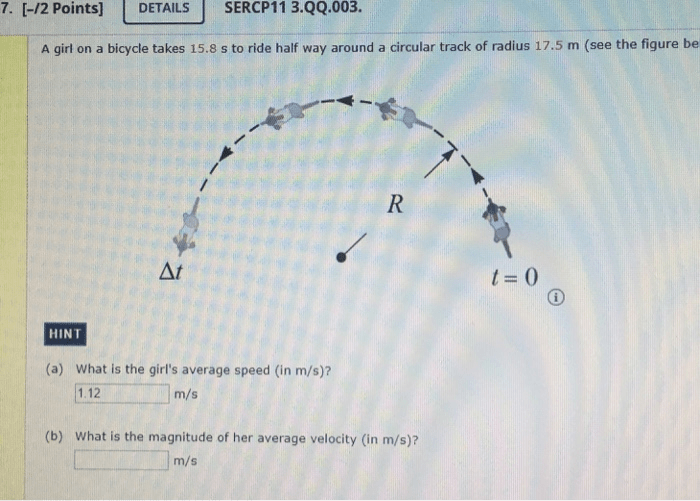
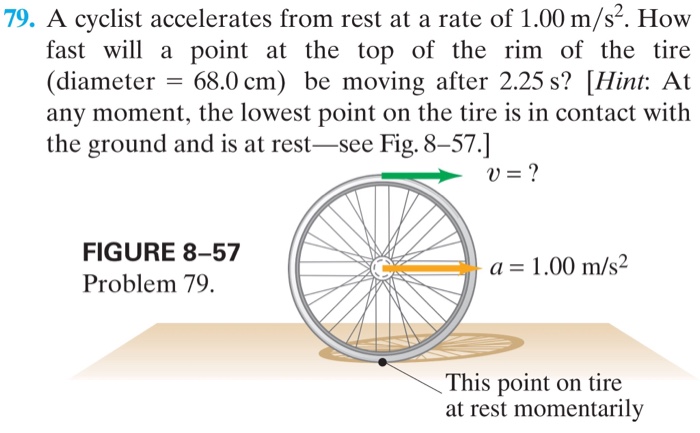
A bicycle takes 8.0 seconds to accelerate from rest to a certain speed. This acceleration, a measure of how quickly the bicycle’s velocity changes over time, is influenced by a multitude of factors, including rider weight, bike weight, terrain, and wind resistance.
Understanding these factors and their impact on acceleration is crucial for optimizing bike design, training strategies, and overall cycling performance.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the concept of acceleration, examining its measurement units and the equation used to calculate it. We analyze the motion of a bicycle as it accelerates, considering the interplay of force, mass, and velocity.
Furthermore, we identify the factors that can affect acceleration and provide data and examples to support our discussion.
Acceleration Basics

Acceleration is the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. The SI unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s²).
Acceleration can be calculated using the following equation:
a = (vf
vi) / t
where:
- a is acceleration (m/s²)
- v fis the final velocity (m/s)
- v iis the initial velocity (m/s)
- t is the time interval (s)
For example, if a bicycle accelerates from rest to a speed of 10 m/s in 2 seconds, its acceleration is 5 m/s².
Motion of a Bicycle, A bicycle takes 8.0 seconds to accelerate
When a bicycle accelerates, its motion is described by the following equation:
v = u + at
where:
- v is the final velocity (m/s)
- u is the initial velocity (m/s)
- a is the acceleration (m/s²)
- t is the time interval (s)
This equation shows that the final velocity of the bicycle is equal to its initial velocity plus the product of its acceleration and the time interval.
The force that causes a bicycle to accelerate is the force applied by the rider’s legs on the pedals. The mass of the bicycle and rider also affects its acceleration. A heavier bicycle and rider will require more force to accelerate than a lighter bicycle and rider.
The terrain on which the bicycle is riding can also affect its acceleration. A bicycle will accelerate more slowly on a hill than on a flat surface.
Wind resistance can also affect a bicycle’s acceleration. A bicycle will accelerate more slowly into a headwind than with a tailwind.
Factors Affecting Acceleration
The following factors can influence the acceleration of a bicycle:
- Rider weight
- Bike weight
- Terrain
- Wind resistance
Rider weight has a direct impact on acceleration. A heavier rider will require more force to accelerate than a lighter rider. This is because the force required to accelerate an object is directly proportional to its mass.
Bike weight also has a direct impact on acceleration. A heavier bike will require more force to accelerate than a lighter bike. This is because the force required to accelerate an object is directly proportional to its mass.
Terrain can also affect acceleration. A bicycle will accelerate more slowly on a hill than on a flat surface. This is because the force of gravity is acting against the bicycle’s motion.
Wind resistance can also affect acceleration. A bicycle will accelerate more slowly into a headwind than with a tailwind. This is because the wind resistance is acting against the bicycle’s motion.
Methods for Measuring Acceleration
There are several different methods for measuring the acceleration of a bicycle.
- Accelerometer
- Speedometer
- Timing gate
An accelerometer is a device that measures the acceleration of an object. Accelerometers can be attached to the bicycle frame or to the rider’s body.
A speedometer is a device that measures the speed of an object. Speedometers can be used to measure the acceleration of a bicycle by measuring the change in speed over time.
A timing gate is a device that measures the time it takes for an object to pass through a certain distance. Timing gates can be used to measure the acceleration of a bicycle by measuring the time it takes to travel a certain distance.
Applications of Bicycle Acceleration
Understanding bicycle acceleration can be useful for a variety of purposes.
- Improving bike design
- Developing training strategies
- Analyzing race data
By understanding the factors that affect bicycle acceleration, engineers can design bikes that are more efficient and faster. Coaches can use acceleration data to develop training strategies that help riders improve their performance. And race analysts can use acceleration data to analyze race results and identify areas for improvement.
Q&A: A Bicycle Takes 8.0 Seconds To Accelerate
What is acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
What is the equation for acceleration?
The equation for acceleration is a = (v – u) / t, where ‘a’ is acceleration, ‘v’ is final velocity, ‘u’ is initial velocity, and ‘t’ is time.
What are the factors that affect bicycle acceleration?
The factors that affect bicycle acceleration include rider weight, bike weight, terrain, and wind resistance.