Select all that are true of a vascular spasm, a condition characterized by the sudden constriction of blood vessels, can have a wide range of causes and symptoms. This article delves into the complexities of vascular spasms, exploring their causes, diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications.
Vascular spasms can affect blood vessels in various parts of the body, leading to a diverse range of symptoms. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and risk factors associated with vascular spasms is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Vascular Spasm
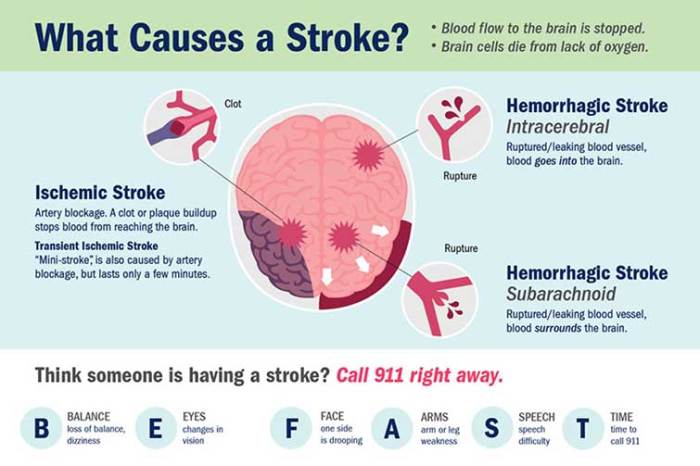
A vascular spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of blood vessels, which can reduce or block blood flow to a particular area of the body. This can lead to a range of symptoms, depending on the location and severity of the spasm.
Symptoms, Select all that are true of a vascular spasm
- Sudden, severe pain
- Numbness or tingling
- Weakness or paralysis
- Vision changes
- Speech difficulties
The symptoms of a vascular spasm can vary depending on the location of the spasm. For example, a spasm in the coronary arteries can cause chest pain and shortness of breath, while a spasm in the brain can cause a stroke.
Causes
- Head injury
- Brain tumor
- Aneurysm
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Stroke
The underlying mechanisms that trigger vascular spasms are not fully understood, but they are thought to involve the release of certain chemicals, such as serotonin and thromboxane, which cause blood vessels to constrict.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of a vascular spasm is based on a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. The doctor may also order imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
- Medications to relax blood vessels
- Surgery to remove the cause of the spasm
- Interventional radiology procedures to open up the blocked blood vessels
The treatment of a vascular spasm depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms.
Complications
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Kidney failure
- Death
The complications of a vascular spasm can be serious, depending on the location and severity of the spasm.
Prevention
- Controlling blood pressure
- Managing cholesterol levels
- Quitting smoking
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent vascular spasms, including controlling blood pressure, managing cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet.
Prognosis
The prognosis for a vascular spasm depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. If the spasm is treated promptly, the prognosis is generally good.
Related Conditions
- Migraine
- Raynaud’s disease
- Scleroderma
- Vasculitis
Vascular spasms can be caused by a number of other medical conditions, including migraine, Raynaud’s disease, scleroderma, and vasculitis.
Research and Advancements
There is currently a great deal of research being conducted on vascular spasms. This research is focused on developing new and more effective treatments for this condition.
Clarifying Questions: Select All That Are True Of A Vascular Spasm
What are the common symptoms of a vascular spasm?
Symptoms may vary depending on the location of the spasm but can include pain, numbness, tingling, weakness, and discoloration of the affected area.
What are the most common causes of vascular spasms?
Common causes include smoking, caffeine, cold exposure, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions such as hypertension and atherosclerosis.
How are vascular spasms diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging techniques such as ultrasound, angiography, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What are the treatment options for vascular spasms?
Treatment depends on the severity and underlying cause and may include medications, lifestyle modifications, or surgical interventions.

