Anatomic pathology focuses on weegy, the meticulous examination of tissues and organs at the microscopic level, playing a pivotal role in diagnosing diseases, guiding treatment decisions, and advancing medical knowledge.
Through advanced techniques and expertise, anatomic pathology provides insights into the cellular and structural changes associated with various ailments, aiding in accurate diagnoses and effective patient management.
Anatomic Pathology: Definition and Scope: Anatomic Pathology Focuses On Weegy

Anatomic pathology is the medical specialty concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the examination of tissues and organs. It plays a crucial role in clinical medicine by providing essential information for patient care, including the identification and characterization of neoplastic and non-neoplastic lesions, inflammatory processes, infectious diseases, and genetic disorders.Anatomic
pathologists examine a wide range of tissues and organs, including biopsies, surgical specimens, and autopsy material. These specimens are processed and prepared for microscopic examination using specialized techniques to preserve their cellular and structural integrity.
Histopathology Techniques
Tissue preparation for histologic examination involves a series of steps, including fixation, dehydration, clearing, and embedding. Fixation preserves the tissue’s morphology and prevents autolysis. Dehydration removes water from the tissue, while clearing makes the tissue transparent for better visualization under the microscope.
Embedding involves infiltrating the tissue with a molten paraffin wax that solidifies upon cooling, creating a solid block that can be sectioned into thin slices.Microscopy is the primary tool used in anatomic pathology to examine tissues. Light microscopy, which uses visible light to illuminate the specimen, is the most commonly used technique.
Electron microscopy, which uses a beam of electrons to generate an image, provides higher resolution and magnification, allowing for the visualization of ultrastructural details.
Gross Examination and Macroscopic Findings
Gross examination involves the macroscopic examination of surgical specimens prior to tissue processing. It includes assessment of the specimen’s size, shape, color, consistency, and any visible lesions or abnormalities. Macroscopic findings can provide valuable information for diagnosis, such as the presence of inflammation, hemorrhage, necrosis, or tumor formation.
Microscopic Examination and Histologic Diagnosis, Anatomic pathology focuses on weegy
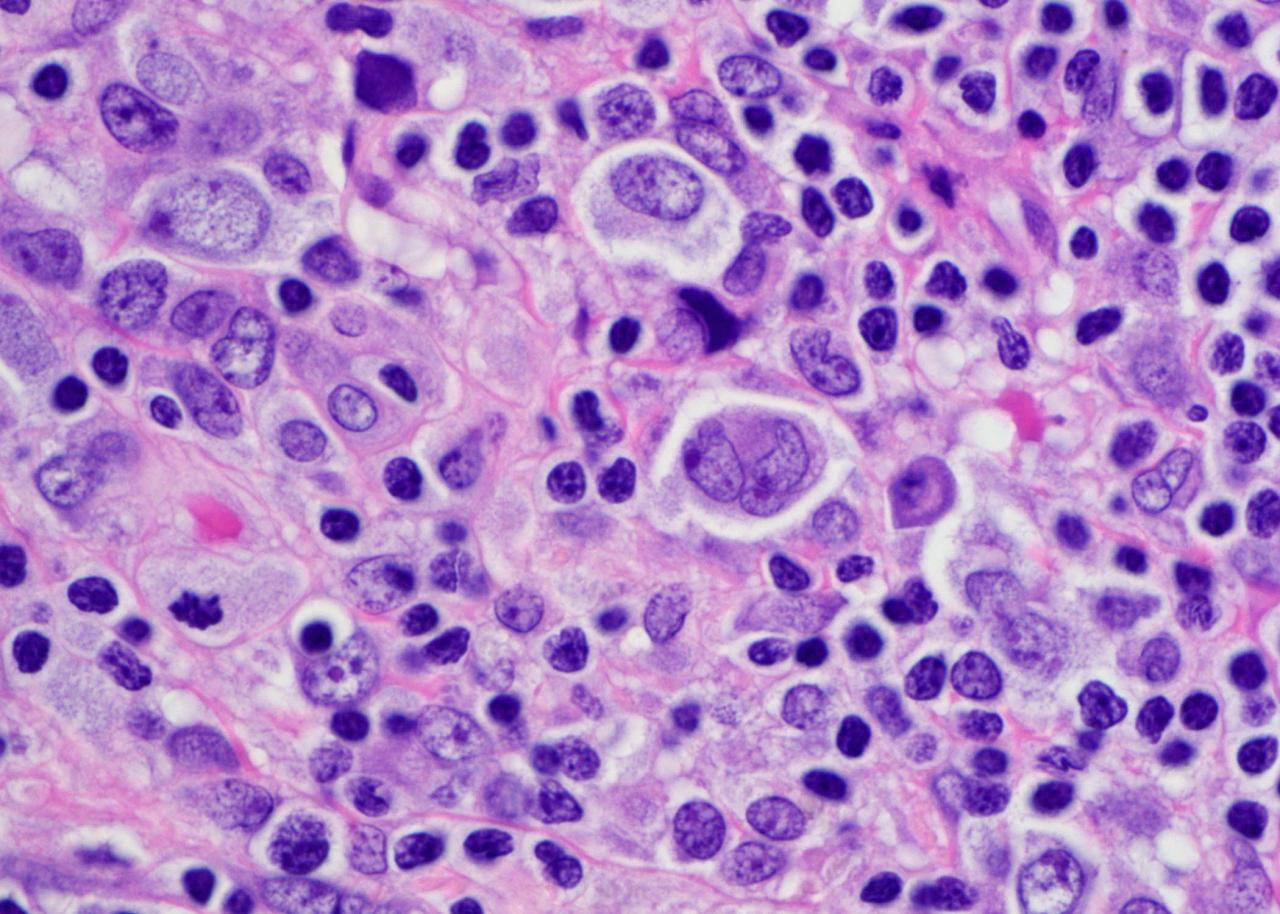
Microscopic examination of tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) is the cornerstone of anatomic pathology. H&E staining allows for the visualization of cellular and structural details, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, and extracellular matrix. Pathologists use a variety of criteria to assess histologic patterns, including cell size, shape, arrangement, and the presence of mitotic figures or other abnormalities.
These findings are used to establish a histologic diagnosis and determine the nature and extent of the disease process.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of gross examination in anatomic pathology?
Gross examination allows pathologists to assess the size, shape, color, and texture of surgical specimens, providing valuable information for diagnosis and guiding further microscopic examination.
How does immunohistochemistry aid in anatomic pathology?
Immunohistochemistry utilizes antibodies to identify specific proteins within tissues, helping pathologists differentiate between normal and abnormal cells and identify the presence of specific diseases.
What is the role of molecular pathology in anatomic pathology?
Molecular pathology involves the analysis of DNA and RNA to detect genetic alterations associated with diseases, providing insights into disease mechanisms and guiding targeted therapies.