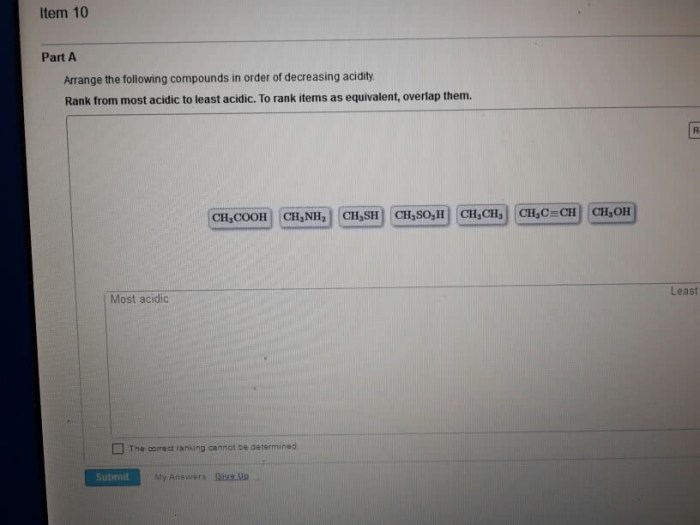
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity – Ranking compounds in order of decreasing acidity is a fundamental concept in chemistry that underpins various applications in organic chemistry, drug design, catalysis, and materials science. This guide delves into the intricacies of acidity, exploring the factors that influence it and the methods used to determine the acidity of compounds.
Acidity, a measure of a compound’s ability to donate protons, is a crucial property that governs chemical reactivity and molecular interactions. Understanding the relative acidity of compounds is essential for predicting reaction outcomes, designing effective catalysts, and developing new materials with tailored properties.
Rank the Following Compounds in Order of Decreasing Acidity
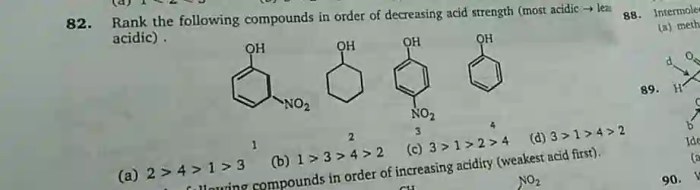
Acidity is a measure of the ability of a compound to donate a proton (H+ ion). The more easily a compound can donate a proton, the more acidic it is. Acidity is typically measured using the pH scale, which ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 0 indicates a very acidic solution, while a pH of 14 indicates a very basic solution.
A pH of 7 is neutral.
The purpose of ranking compounds in order of decreasing acidity is to determine which compounds are more likely to donate protons and which are less likely to donate protons. This information can be useful for a variety of purposes, such as designing new drugs, catalysts, and materials.
Factors Affecting Acidity
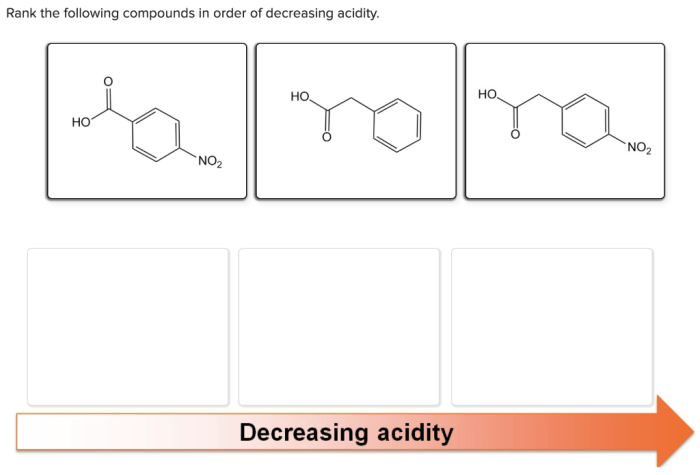
There are a number of factors that affect the acidity of a compound. These factors include:
- The strength of the conjugate acid-base pair.The conjugate acid of a base is the acid that is formed when the base accepts a proton. The conjugate base of an acid is the base that is formed when the acid donates a proton. The stronger the conjugate acid, the weaker the base, and vice versa.
- The electronegativity of the atom that is bonded to the hydrogen atom.Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons. The more electronegative the atom, the more strongly it will attract the electrons in the O-H bond, and the weaker the O-H bond will be. This means that compounds with more electronegative atoms bonded to the hydrogen atom will be more acidic.
- The hybridization of the atom that is bonded to the hydrogen atom.Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new orbitals with different shapes and energies. The hybridization of the atom that is bonded to the hydrogen atom can affect the strength of the O-H bond. For example, sp3-hybridized carbon atoms form stronger O-H bonds than sp2-hybridized carbon atoms.
This means that compounds with sp3-hybridized carbon atoms bonded to the hydrogen atom will be less acidic than compounds with sp2-hybridized carbon atoms bonded to the hydrogen atom.
- Resonance.Resonance is the delocalization of electrons over multiple atoms. Resonance can stabilize the conjugate base of an acid, which makes the acid less likely to donate a proton. This means that compounds with resonance-stabilized conjugate bases will be less acidic than compounds without resonance-stabilized conjugate bases.
Methods for Ranking Acidity
There are a number of methods that can be used to rank compounds in order of decreasing acidity. These methods include:
- The pKa value.The pKa value of an acid is the negative logarithm of its acid dissociation constant (Ka). The Ka value is a measure of the strength of an acid. The lower the pKa value, the stronger the acid. This means that compounds with lower pKa values will be more acidic than compounds with higher pKa values.
- The Hammett acidity function (H0).The Hammett acidity function (H0) is a measure of the acidity of a solution. The H0 value is a measure of the concentration of protons in a solution. The higher the H0 value, the more acidic the solution. This means that compounds that are dissolved in solutions with higher H0 values will be more acidic than compounds that are dissolved in solutions with lower H0 values.
- Equilibrium constants.Equilibrium constants are measures of the relative amounts of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The equilibrium constant for an acid-base reaction is a measure of the strength of the acid. The larger the equilibrium constant, the stronger the acid.
This means that compounds with larger equilibrium constants will be more acidic than compounds with smaller equilibrium constants.
- Reaction rates.Reaction rates are measures of the speed of a chemical reaction. The reaction rate for an acid-base reaction is a measure of the strength of the acid. The faster the reaction rate, the stronger the acid. This means that compounds with faster reaction rates will be more acidic than compounds with slower reaction rates.
Examples of Ranked Compounds
The following table shows a list of compounds ranked in order of decreasing acidity:
| Compound | pKa |
|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid | -7.0 |
| Sulfuric acid | -3.0 |
| Nitric acid | -1.4 |
| Acetic acid | 4.76 |
| Benzoic acid | 4.20 |
| Ethanol | 15.9 |
| Water | 15.7 |
As can be seen from the table, hydrochloric acid is the most acidic compound, followed by sulfuric acid, nitric acid, acetic acid, benzoic acid, ethanol, and water. This ranking is consistent with the factors that affect acidity discussed above.
Applications of Acidity Ranking
Acidity ranking is an important tool in organic chemistry. It can be used to design new drugs, catalysts, and materials. For example, acidity ranking can be used to design drugs that are more effective at targeting specific receptors. It can also be used to design catalysts that are more efficient at catalyzing specific reactions.
Additionally, acidity ranking can be used to design materials that are more resistant to corrosion.
FAQ Explained: Rank The Following Compounds In Order Of Decreasing Acidity
What is the relationship between pKa and acidity?
pKa is a measure of acidity, representing the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka). A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid, as it dissociates more readily in water to release protons.
How does electronegativity affect acidity?
Electronegativity measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons. More electronegative atoms stabilize negative charge better, making the conjugate base more stable and the acid stronger.
What is the role of resonance in acidity?
Resonance delocalizes charge over multiple atoms, stabilizing the conjugate base. This stabilization effect enhances acidity by making it easier for the acid to donate a proton.