Complete these nuclear reactions with the particle that is emitted. This fundamental aspect of nuclear physics involves understanding the emission of particles during nuclear reactions and balancing nuclear equations to ensure conservation laws are upheld. Nuclear reactions find applications in diverse fields, including nuclear power and medical imaging, making it a topic of paramount importance.
Nuclear reactions involve transformations of atomic nuclei, often accompanied by the release of energy and emission of particles. Radioactive decay, a specific type of nuclear reaction, plays a crucial role in various scientific disciplines and technological advancements.
1. Basic Concepts: Complete These Nuclear Reactions With The Particle That Is Emitted.
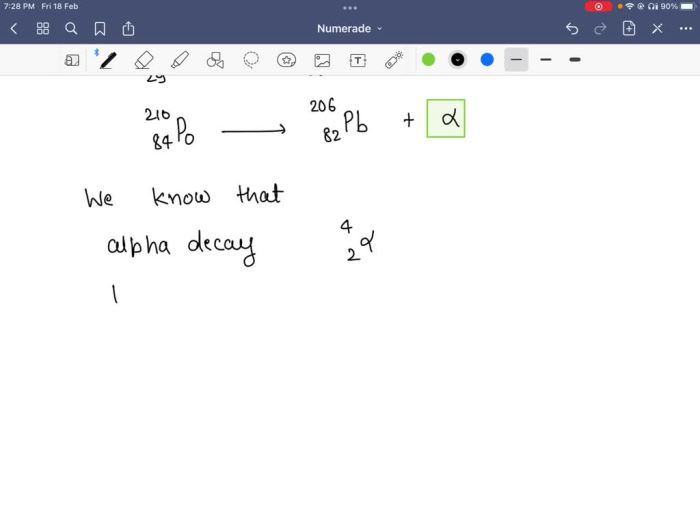
Nuclear reactions involve the transformation of atomic nuclei, releasing or absorbing energy. They occur when a nucleus interacts with another particle, such as a neutron or proton. The fundamental principle is that the total mass and charge of the reactants must equal the total mass and charge of the products.
Radioactive decay is a type of nuclear reaction where an unstable nucleus emits radiation to reach a more stable state. This process results in the emission of particles like alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays.
Nuclear reactions can be classified into various types, including:
- Nuclear fission: Splitting of a heavy nucleus into lighter nuclei.
- Nuclear fusion: Combining two light nuclei into a heavier nucleus.
- Nuclear scattering: Elastic or inelastic collisions between a nucleus and a particle.
2. Completing Nuclear Reactions
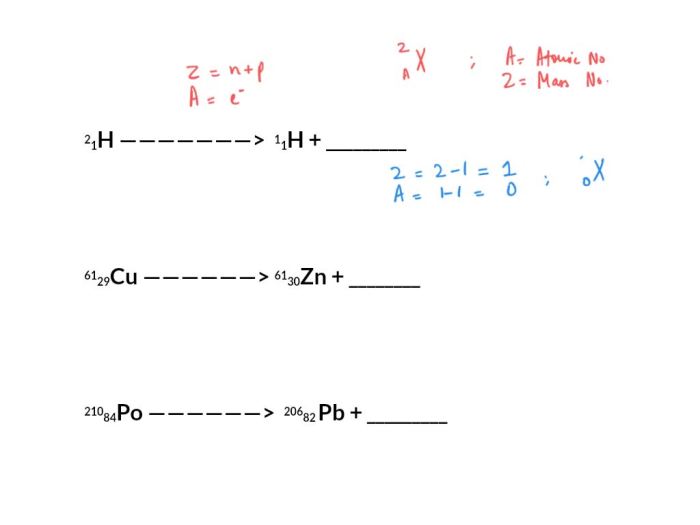
Balancing nuclear equations involves identifying the missing particle emitted in the reaction. The conservation laws of mass, charge, and energy must be satisfied.
Experimental techniques like particle detectors and spectrometers help determine the emitted particle. Theoretical models also play a crucial role in predicting reaction outcomes.
3. Methods for Completing Reactions
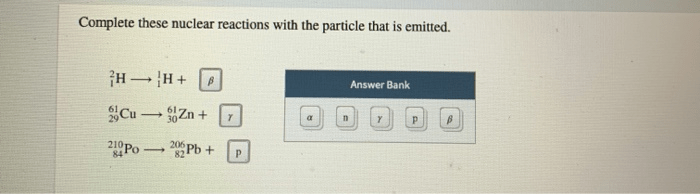
Experimental techniques used to determine the emitted particle include:
- Particle detectors: Detect and identify charged particles based on their energy loss and trajectory.
- Spectrometers: Measure the energy and momentum of emitted particles.
Theoretical models provide predictions about reaction outcomes based on nuclear physics principles. These models can guide experimental design and interpret results.
4. Applications and Examples

Nuclear reactions have practical applications in various fields:
- Nuclear power: Generating electricity by harnessing the energy released from nuclear reactions.
- Medical imaging: Using radioactive isotopes for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- Nuclear astrophysics: Studying the role of nuclear reactions in stars and other celestial objects.
Specific examples of nuclear reactions and their applications include:
- Uranium-235 fission: Used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
- Carbon-14 dating: Determining the age of organic materials using the decay of carbon-14.
- Positron emission tomography (PET): Using radioactive isotopes to image metabolic activity in the body.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of identifying emitted particles in nuclear reactions?
Identifying emitted particles is crucial for understanding the type of nuclear reaction, balancing nuclear equations, and predicting reaction outcomes.
How are emitted particles detected in nuclear reactions?
Particle detectors and spectrometers are commonly used to detect and analyze emitted particles in nuclear reactions.
What are the practical applications of nuclear reactions?
Nuclear reactions have applications in nuclear power generation, medical imaging, cancer treatment, and various scientific research fields.